Laudis
title-product-highlights
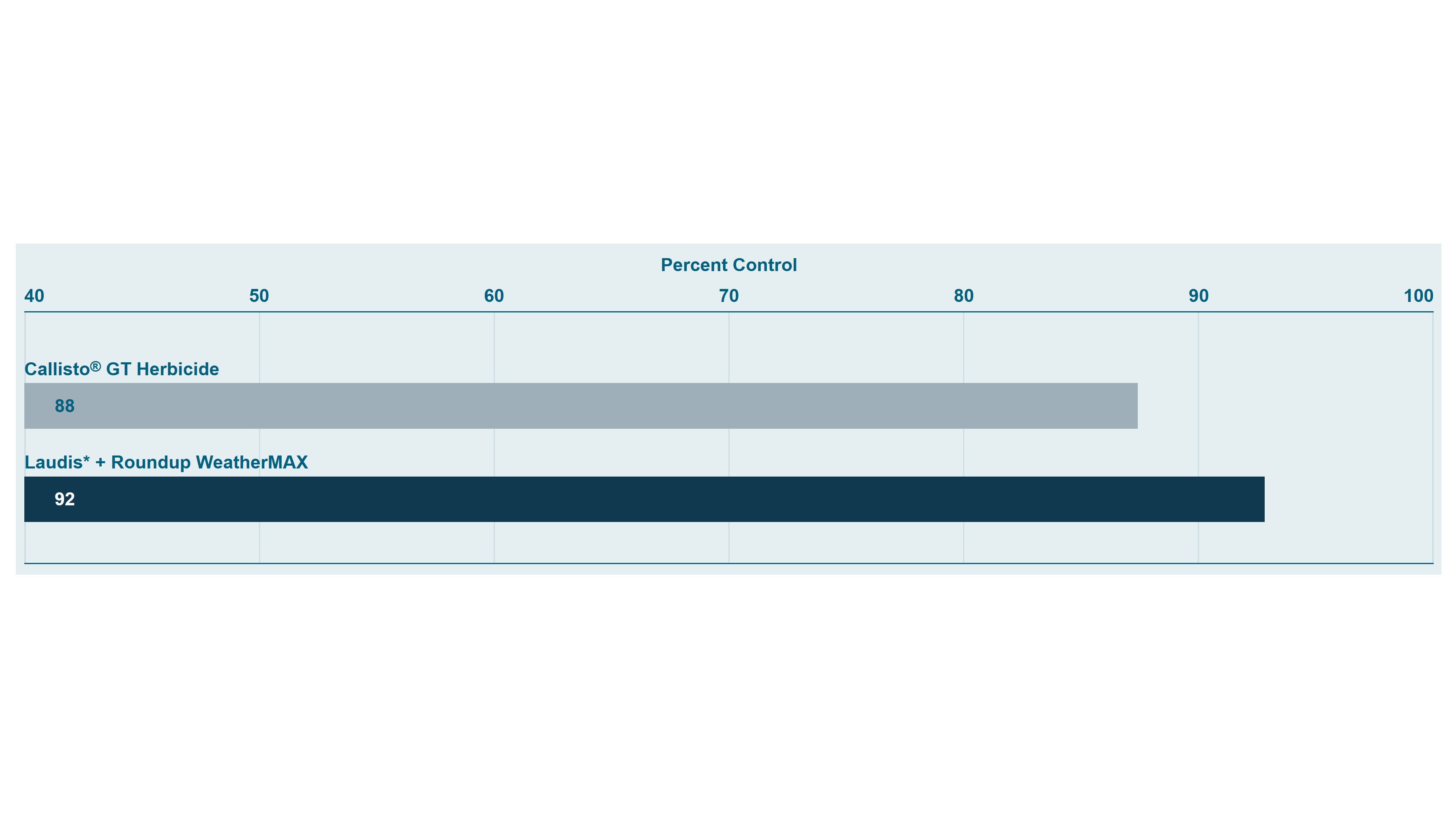
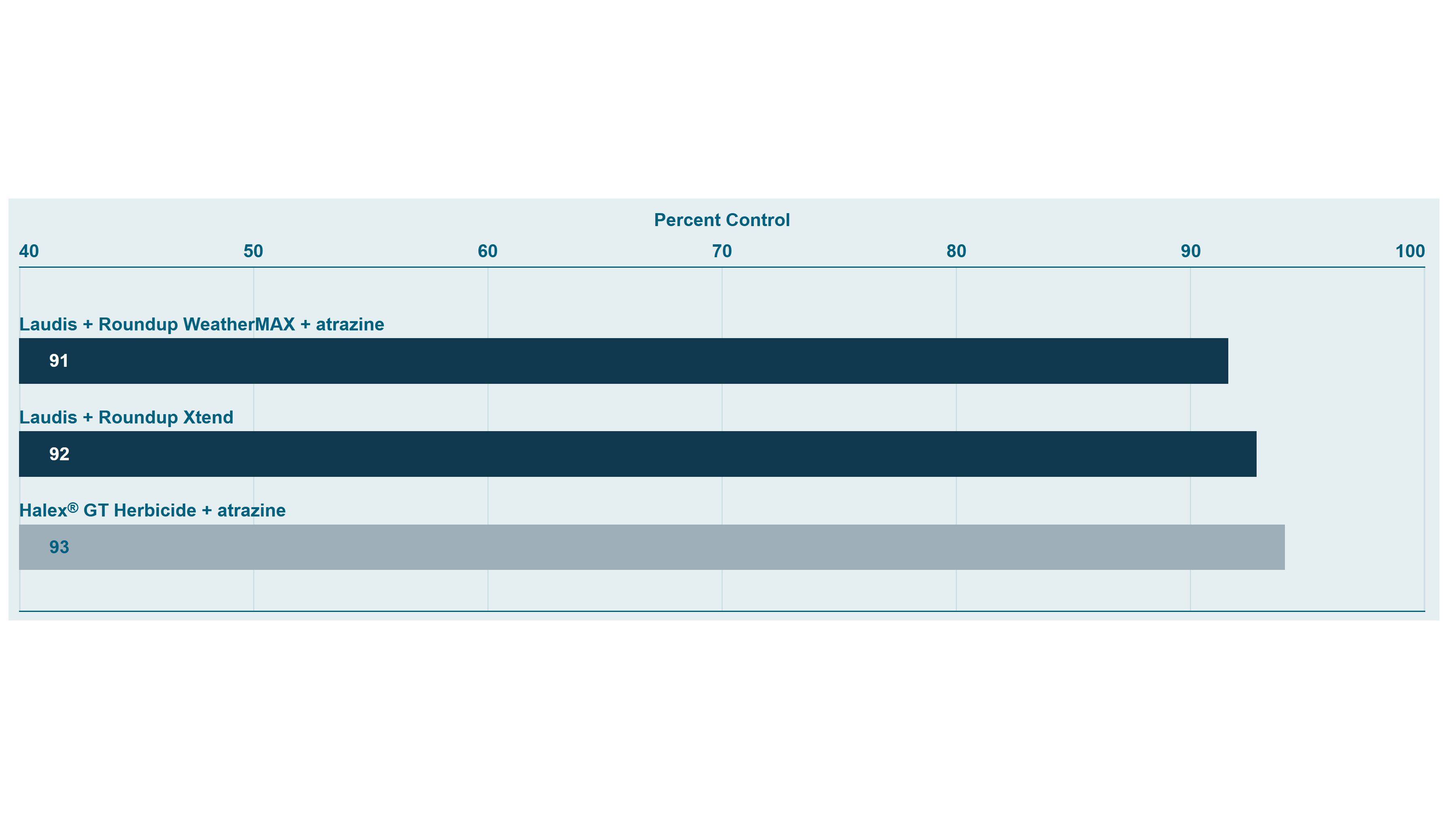
Excellent post emergence broadleaf control, including tough to control glyphosate-resistant weeds such as Canada fleabane, giant ragweed and waterhemp
Built-in safener for exceptional crop safety on field corn, seed corn and sweet corn types with favorable rotation intervals
Rapid burndown and up to 3 weeks of residual activity at the high rate of 220 mL/ha (89 mL/ac.)
Excellent resistance management tool and tank-mix partner with Pardner® herbicide and Roundup® herbicide brands
product-details-heading
| crops | category | groups-active-ingredients | formulation-type | packaging |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Corn (Field, Seed, Sweet) | Broadleaf & Grass Weeds | 27 Tembotrione | Suspension Concentrate | 3.6 L jug |
| crops |
|---|
Corn (Field, Seed, Sweet) |
| category |
|---|
Broadleaf & Grass Weeds |
| groups-active-ingredients |
|---|
27 Tembotrione |
| formulation-type |
|---|
Suspension Concentrate |
| packaging |
|---|
3.6 L jug |
| weeds-controlled | weeds-suppressed |
|---|---|
Canada fleabane1 Hairy galinsoga1 Kochia1 Common lamb’s-quarters1 Redroot pigweed1 | Wild buckwheat Giant foxtail Green foxtail |
| weeds-controlled |
|---|
Canada fleabane1 Hairy galinsoga1 Kochia1 Common lamb’s-quarters1 Redroot pigweed1 |
| weeds-suppressed |
|---|
Wild buckwheat Giant foxtail Green foxtail |
Performance Data
title-use-mixing